“TL;DR: Asiaticoside, an active from gotu kola / centella asiatica, has been found to reverse oxidative damage and senescence in endothelial (blood vessel lining) cells.
Cellular senescence of the adipose tissue, connective tissue and blood vessels is an important and largely unexplored cause of cellulite. Oxidative damage is an established cause of cellulite.”
The Centella asiatica active Asiaticoside eliminates free radical damage in blood vessels
Asiaticoside from Gotu Kola prevents oxidative damage and reverses all markers of oxidation in endothelial cells
In addition, asiaticoside partially reverses cell senescence
Asiaticoside in cellulite creams and nutritional supplements
Asiaticoside Prevents Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Endothelial Cells by Activating ROS-dependent p53/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway
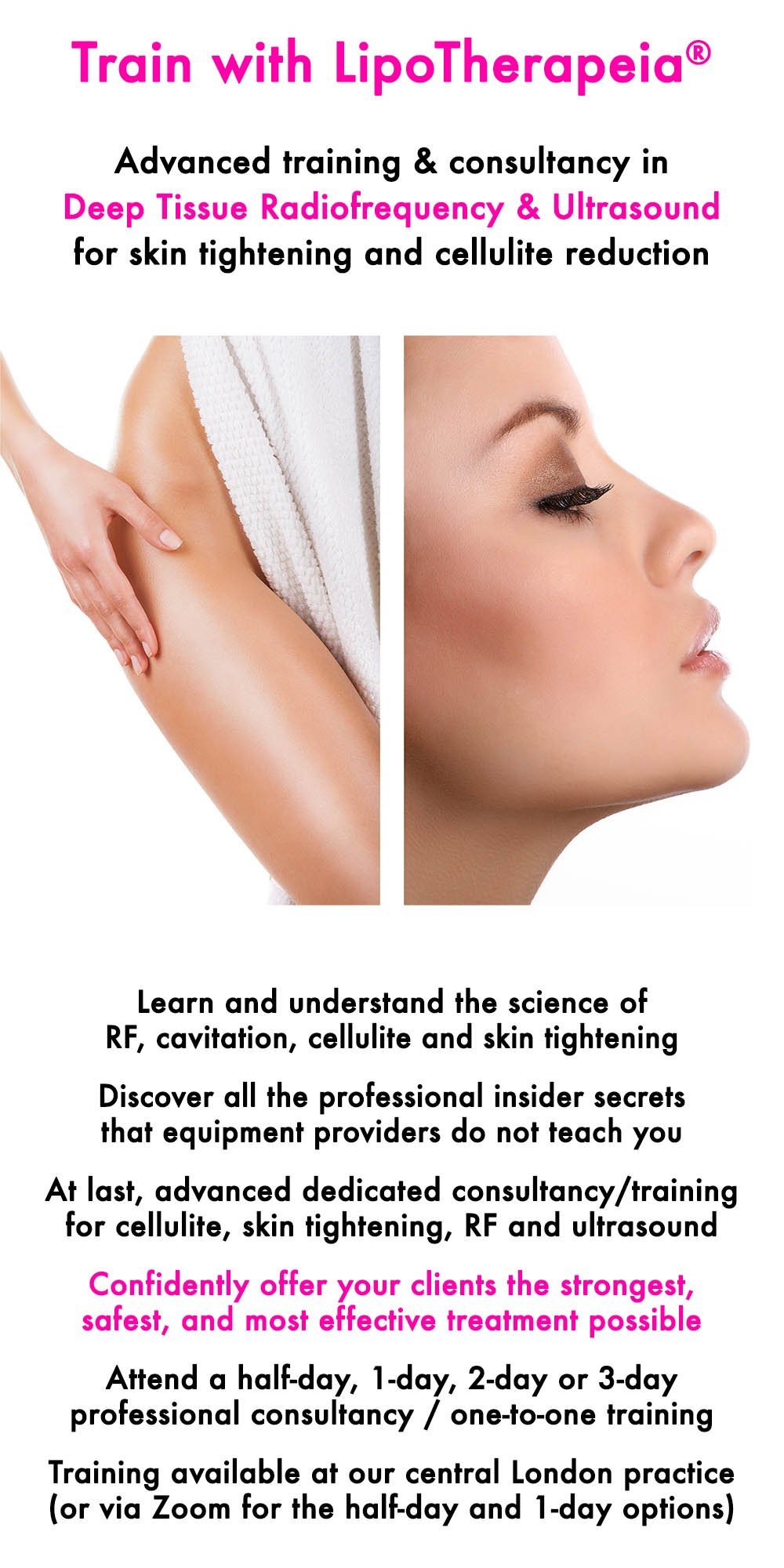
Have a skin tightening/cellulite treatment in London with the experts
Discover our professional training in cellulite, skin tightening, radiofrequency and ultrasound
Asiaticoside from Gotu Kola prevents oxidative damage and reverses all markers of oxidation in endothelial cells
Asiaticoside and the other three centella asiatica main active molecules (asiatic acid, madecassic acid, asiaticoside and madecassoside) are known for their multiple action against whole body ageing, skin ageing and cellulite.
In this new study of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), asiaticoside was found to reverse all markers of oxidative stress.
Furthermore, asiaticoside restored antioxidant markers, such as SOD (superoxide dismutase), NO (nitric oxide) and GSH-Px (glutathione peroxidase), after oxidative insult.
In addition, asiaticoside partially reverses cell senescence
Plus asiaticoside significantly reversed senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity, a marker of cell senescence. (Senescence is a major cause of ageing and whole body inflammation - and consequently cellulite.)
Given its anti-senescence properties, asiaticoside can be used as part of anti-senescence / senolytic regime for blood vessels and entire body.
Asiaticoside in cellulite creams and nutritional supplements
Cellular senescence is an important aspect of cellulite, especially senescence of blood vessels, skin and adipose tissue. Asiaticoside, and most probably the other three gotu kola triterpenes too, help reverse senescence.
Furthermore, gotu kola helps fight cellulite via multiple other pathways, including fibrosis, inflammation, glycation and oxidative stress reduction.
So the anti-senescence action of asiaticoside, adds yet another way in which gotu kola / centella asiatica helps prevent / reduce cellulite.
Asiaticoside can be found in:
Proper, therapeutic concentrations in a very small number of quality anti-cellulite and anti-aging creams (most are very diluted and/or contain low purity active ingredients)
A small number of quality centella asiatica / gotu kola nutritional supplements (difficult to source and most are not concentrated enough)
Centella asiatica herbal tea (easy to source on the internet these days)
Asiaticoside Prevents Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Endothelial Cells by Activating ROS-dependent p53/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract: Background: Asiaticoside (AC) is a triterpenoid saponin found in Centella asiatica (L.) Urban extract that has a wide range of pharmacological properties. Our previous study demonstrated that AC could promote angiogenesis in diabetic wounds, but the specific mechanisms remain unknown. Objective: This study aimed to examine the effectiveness and mechanism of AC on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) toxicity. Methods: Senescence was confirmed using senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity and expression of the cell cycle phase markers p16 and p21. The levels of SOD, NO, MDA, GSH-Px, ROS were tested. Furthermore, several cell death-related genes and proteins (p53, Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3) were assessed with RT-qPCR and Western blotting. Results: AC significantly reduced SA-β-gal activity, with both the suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors p16 and p21. We also found that the induced oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by t-BHP treatment resulted in the decrease of antioxidant en-zymes activities, the surge of ROS and MDA, the up-regulation of p53, Bax and caspase-3, and the decrease of SOD, NO, GSH-Px and Bcl-2. These biochemical changes were all reversed by treatment with varied doses of AC. Conclusion: AC alleviates t-BHP-induced oxidative injury and apoptosis in HUVECs through the ROS-dependent p53/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 signaling pathway. It may be a potential antioxidant applied in metabolic disorders and pharmaceutical products.
Have a skin tightening/cellulite treatment in London with the experts
At LipoTherapeia we have specialised 100% in skin tightening and cellulite reduction for more than two decades and 20,000+ sessions.
This is all we study and practise every day and have researched and tried hands-on all the important skin tightening equipment and their manufacturers.
As strong, deep acting radiofrequency and deep-acting, high-power ultrasound cavitation are the technologies of choice for skin tightening and cellulite reduction, we have invested in the best RF/ultrasound technologies in the world.
Furthermore, over the last two decades we have developed advanced RF and cavitation treatment protocols in order to make the most of our technologies, for maximum results, naturally and safely.
Our radiofrequency/ultrasound treatments are comfortable, pain-free, downtime-free, injection-free, microneedling-free, 99.5%+ safe and always non-invasive.
And our focus is on honest, realistic, science-based treatment, combined with caring, professional service, with a smile.
We will be pleased to see you, assess your cellulite, skin laxity or fibrosis, listen to your story, discuss your case and offer you the best possible treatment.
Learn more or check prices and book an expert treatment at our London clinic (49 Marylebone High Street, W1)
Discover our professional training in cellulite, skin tightening, radiofrequency and ultrasound
Do you want to deeply understand radiofrequency, ultrasound cavitation, cellulite and skin tightening?
Attend a half-day, 1-day or 2-day or 3-day professional consultancy / one-to-one masterclass and confidently offer your clients the safest, strongest and most effective treatment possible.
Service available via Zoom or at our central London practice.



![How to get rid of cellulite | 111 tips from the experts [2024 update]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5294cad9e4b009e918124a61/1582205124442-U31A5ECGNCG62VFPPJWJ/How+to+get+rid+of+cellulite+in+2020.jpg)


